Call Us Today - 1 (860) 222-3055
Page 6
Media Contact
Email: media@floodpanel.com


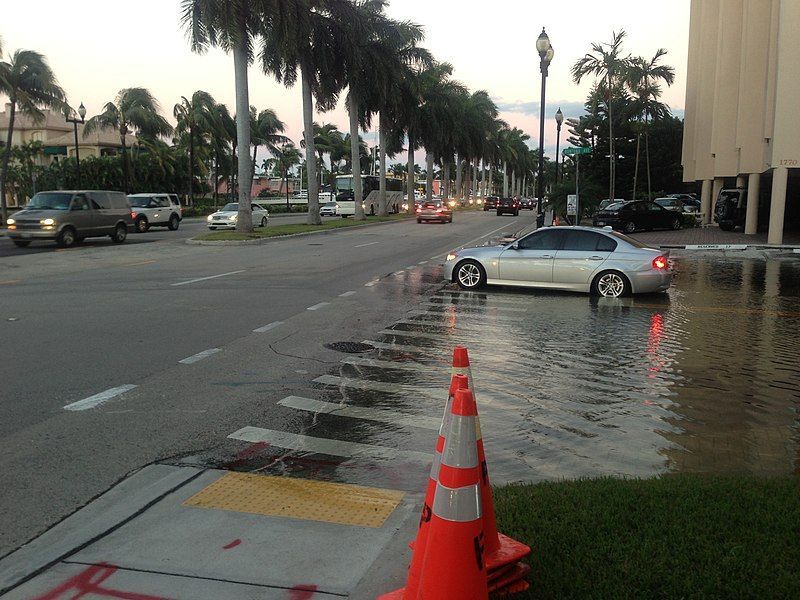
PHOTO: Sunny day high tide nuisance flooding in Brickell, downtown Miami Florida. The morning high tide on October 17, 2016. Roughly 4.0 ft MLLW, +3 ft above MSL, 2 ft NAVD 88, about 1.75 feet MHHW for Miami, Virginia Key tide gauge. This location rounds to 0 meters/0 feet AMSL.
“Sunny Day Flooding”, also known as tidal flooding, is a phenomenon that occurs when low-lying areas are temporarily flooded during periods of unusually high tides, such as during a full moon. This may happen when the sky is clear and sunny, with not a single cloud on the horizon. During a sunny day flood event, streets can be covered by water in an unexpected way, because residents are not prepared for floods in the absence of rain or storms. Nevertheless, this flooding does occur during dry weather, and the frequency of these floods is increasing in an alarming way.
This summer, the federal government issued a warning to those who live in and around low-lying zones. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has identified dozens of communities that will suffer an increase in sunny day floods, from Miami to San Diego. The increase that is expected during the coming year is attributed to an abnormally active El Niño weather pattern, combined with sea level rise that is happening across the globe. Rapidly melting ice caps and glaciers from Antarctica to Greenland continue to feature prominently in news coverage, and videos of huge chunks of polar ice calving into the sea remind us all that we can expect major changes, and soon!
One of those changes is sure to be a flood-filled future. This year, with the hyperactive El Niño weather pattern in play, all types of floods are predicted to be a problem. But the “sunny day flood” brings a special kind of threat, mostly due to the general lack of preparation of those affected. Sea level rise, coupled with sinking coastlines along the eastern seaboard, has greatly increased the number of affected communities. During these “sunny day floods”, roads are often covered by water; and in many cases vital thoroughfares are closed until the water recedes. Flooded roads are subsequently plagued by potholes, erosion of shoulders, and instability of the roadbed, which can lead to washouts.
In addition to road damage, affected communities also suffer many other negative consequences from frequent flooding. Basements and underground parking structures for homes and businesses fill with water again and again, followed by days or weeks of backbreaking clean-up. Storm water systems can become overwhelmed and damaged, and septic systems can overflow, polluting property and waterways. Many homes in rural areas rely on septic systems for disposing of toilet wastewater, so one can only imagine how inconvenient it must be when these systems become temporarily unusable due to flooding.
Low-lying areas are particularly vulnerable, of course, and nowhere in the US is more threatened than Florida. With much of the state at or below 10′ above sea level, every inch lost to sea level rise or subsidence (sinking) of the coastline translates to real hardship for the people living in these areas. After the floods have receded, many homeowners find the rebuilding process to be all but impossible. Flood insurance, for those lucky enough to have it, becomes prohibitively expensive after a series of floods. Insurance companies or community code may suddenly require that a building be raised on stilts, or that repairs shall not be possible at all. Some zones may be declared no longer supported for rehabilitation, and repair of buildings in these areas would become illegal. When that happens, the buildings must by law be left to slowly fall apart by attrition and neglect, even as the property owner may still have to pay a mortgage for the uninhabitable home.
This year may be particularly hard for home and business owners in these low-lying communities. While coastal zones have typically suffered about five days a year of “sunny day flooding”, this record will most likely be smashed during the 2019-20 flood season. But even this is nothing compared to the predictions for 2050, by which time “sunny day floods” are projected to become a very common nuisance. Within the next thirty years, it is thought that many unlucky communities will suffer sunny day floods up to 100 days out of each year!
Source:: FloodBarrierUSA
Neighborhood Fix
David Levy, professor of Management, Director of the Center for Sustainable Enterprise and Regional Competitiveness, University of Massachusetts, warns “beware the big fix.” His team studied the feasibility of constructing a large barrier across Boston Harbor that would deploy large gates to protect the city from storms. The plan would cost the city an estimated $12 billion over 30 years. The study determined the high cost could not be justified in the face of uncertainty about sea-level rise and global warming.
According to Levy, most resiliency projects provide no immediate benefits and are hard to sell to the public. He recommends a “neighborhood-level approach” that includes “upgrades in housing, transportation and infrastructure.” Additionally, investment by private property owners in flood protection measures like flood gates and flood doors would lessen the public burden.
Some cities have taken steps in this direction. Last year, Miami voters approved a $400 million bond to pay for resiliency projects. In Harris County, Texas, voters still rebuilding after Hurricane Harvey approved $2.5 billion for flood protection. In San Francisco, a $425 million bond to shore up a sea wall was approved. (Read Levy’s article here, theconversation.com/climate-change-resilience-could-save-trillions-in-the-long-run-but-finding-billions-now-to-pay-for-it-is-the-hard-part-108143).
Nuisance Flood Threat
It’s not just major storms that threaten cities. Frequent nuisance flooding in Atlantic City, New Jersey and Annapolis, Maryland is taking an economic toll. According to a Stanford University study, Annapolis lost as much as $172,000 due to 3,000 missed customer visits in 2017 due to flooded businesses. (Read more here, www.bdcnetwork.com/persistent-flooding-having-economic-impact-coastal-cities.)
The most vulnerable cities seem to understand that the climate is changing and they are making efforts to prepare for what’s coming. Given the intensity of recent storms, the sooner the better.
Photo credit: By Edgar El, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=60246822
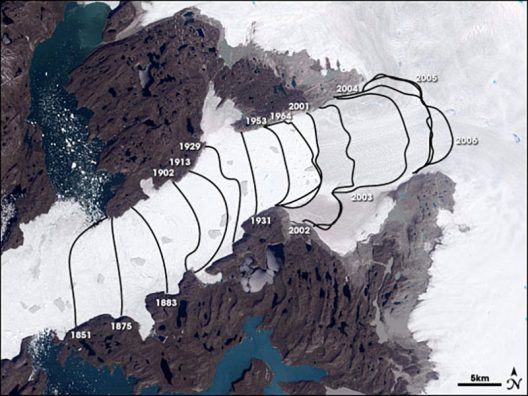
Scientists have learned that the glaciers of Greenland and Antarctica are melting far faster than previously suspected, creating a flooding hazard to coastal communities all over the world. It is now known that many glaciers that appear to be healthy and solid from above are in fact melting from within, below the surface. This subsurface rot is suddenly revealed when huge glacier formations suddenly fracture, revealing a large empty space beneath, where the ice has already melted. A good analogy is to think of a decayed tooth. The tooth may look and feel strong, but if a cavity lurks beneath the healthy enamel, it can eat away at the tooth from inside, until it one day breaks apart. This is currently happening to huge glaciers in various parts of the world.
There is one place on earth that is causing the most concern regarding global warming in general and melting glaciers in particular. This is the great frozen island of Greenland, which is entirely covered by a huge ice sheet. For reasons not yet fully understood, the glacial ice sheet that covers Greenland is melting much faster than other glaciers. The melting and fracturing of massive glaciers in Antarctica has been reported in the news frequently, with alarming video of enormous icebergs calving and breaking apart. One glacier on the Larsen Sea Shelf calved a stupefyingly huge chunk in late 2018, and the iceberg that broke off was more than four times the size of Manhattan! As scary as this Antarctic melt truly is, the melt that is taking place in Greenland is even worse.
This Landsat data image shows how the Jakobshavn-Isbræ glacier retreated, from left to right, up the Ilulissat fjord between 1851 and 2006. Courtesy NASA Earth Observatory
But all this melting of glaciers and calving of icebergs is not causing hazards exclusively on a local basis. It is not only polar bears and walruses that will be negatively affected by this rapid melt. The freshwater that is pouring into our seas from the melted glaciers in Greenland is creating many, many other threats — up to our own front door, thousands of miles away. For example, the introduction of all this suddenly unlocked freshwater affects salinity, ocean currents, atmospheric conditions, and of course, sea level rise. All these factors affect much more than our oceans!
By the end of this century, it is expected that the planet will see a sea level rise of between half a meter and two meters, or perhaps even more. We have all seen the scary projected maps showing half of Florida swallowed by the sea, but unless we live on the Florida coastline, many of us still continue to underestimate the devastation that sea level rise will bring to all of us. In addition to losing millions of homes, farms, businesses, harbors, infrastructure, and even fisheries, sea level rise will also impact all of us by putting into motion the forces that create stronger and more frequent hurricanes, tornadoes, droughts, monsoons, and even wildfires. In short, we will all be affected, to some extent, by the glaciers melting in Greenland, no matter where we live.
While the worst of this dire future remains outside the life span of people alive today (and it is hoped that corrective measures may be able to reverse or slow the threats) some of these effects are already being felt today. Sea level rise is indisputably eating away at our coastal communities, and flooding is an ever greater threat with each year that goes by. Fortunately, great innovations in the area of flood defense are giving businesses and homeowners important flood-fighting weapons in the struggle against floods. Even as floods become more powerful and frequent, so the flood barriers are constantly being improved and adapted to stay one step ahead of the threat.
Source:: FloodBarrierUSA
A new article (https://www.popsci.com/sea-levels-rising-unevenly) recently published by Popular Science explains some quirks of sea level rise in a way that is easy for non-scientists to understand. The author, Marlene Cimons, uses a see-saw metaphor to help us to visualize the forces at work as changes in sea level affects the coastline differently in different areas.
The average lay person probably envisions sea level rise as a uniform phenomenon that simply increases the volume of the ocean, causing it to encroach the land masses equally all around the globe. But this is not how it happens in reality, and Ms. Cimon’s article helps us to understand why, as she describes the natural process that is called ‘post-glacial rebound’.
When a large glacier covers a land mass, the extreme weight of the huge ice feature weighs down the land under the glacier, but the ice-free edges are squeezed upwards. We can easily visualize this by thinking of the see-saw: when one side is down, the other side must go up. If we push on a water balloon, for example, the center of the ballon goes down but the edges go up. Over a long period of time the glacial ice has melted, and the weight has been lifted off the land. This results in the formerly weighed-down land springing back up, with the previously uplifted land sinking back down. Of course, none of this happens quickly, so in this sense the see-saw comparison is misleading. Even though the glaciers that once covered much of the northeastern U.S. have disappeared thousands of years ago, the land is today still see-sawing slowly in response to the changes created by the melting.
NOAA’s Coastal Flood Exposure Mapper is an online tool that allows the user to create and share maps of sea level rise and flooding, and view the potential populations impacted.
So in our present day we have land that is slowly rising in some places and slowly sinking in other places. This movement is not perceptible to us, and yet it is happening quickly enough that it can be measured during our lifetime. It is due to this post-glacial rebound that areas such as the Chesapeake Bay region are experiencing faster and more extreme sea level rise than an area that was not affected by glaciers. This region was historically located at the uplifted edges of a glacier during the distant past, and is now sinking, while simultaneously being inundated by sea level rise. These two factors, working together, make these areas of land much more likely to be inundated, because they are physically sinking at the same time that sea level rise is encroaching the entire coastline.
We now know with a high degree of certainty that this sea level rise is caused primarily by two things: the melting ice caps that are adding unfathomable amounts of fresh water into the oceans, and the warming of the oceans themselves, which physically expands the water. These forces, combined with the post-glacial settling of certain geographical areas, all work together to make it appear that some zones are being inundated at a much faster rate. These areas are today serving as canaries in the coal mine, and the alarming loss of land in these zones is perhaps waking up communities that are currently less affected.
With sea level rise speeding up measurably (and observably) even during one human lifetime, the need for flood defense and long-term planning has reached a critical status. Communities and municipalities that fail to learn from what is happening in Norfolk, Virginia will pay dearly in the near future. Zones that were formerly not known to flood will soon be suffering unspeakable flood damage and devastation if prudent measures are not put into place NOW.
Source: FloodBarrierUSA

Tell us about your project
We look forward to the opportunity to earn your business and to become a value-added partner on your design and construction team.
Contact Us
Contact Us
Phone:
1-860-222-3055
Address: 1555 Jupiter Park Drive, Suite 5, Jupiter, FL 33458

